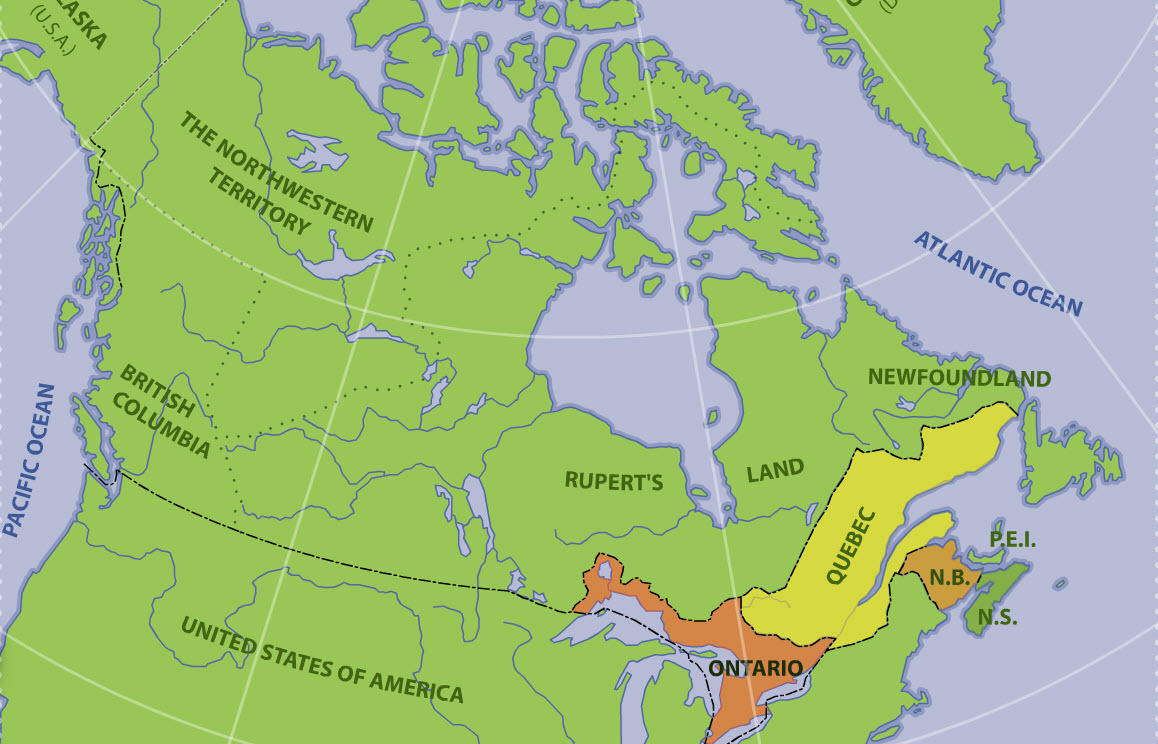
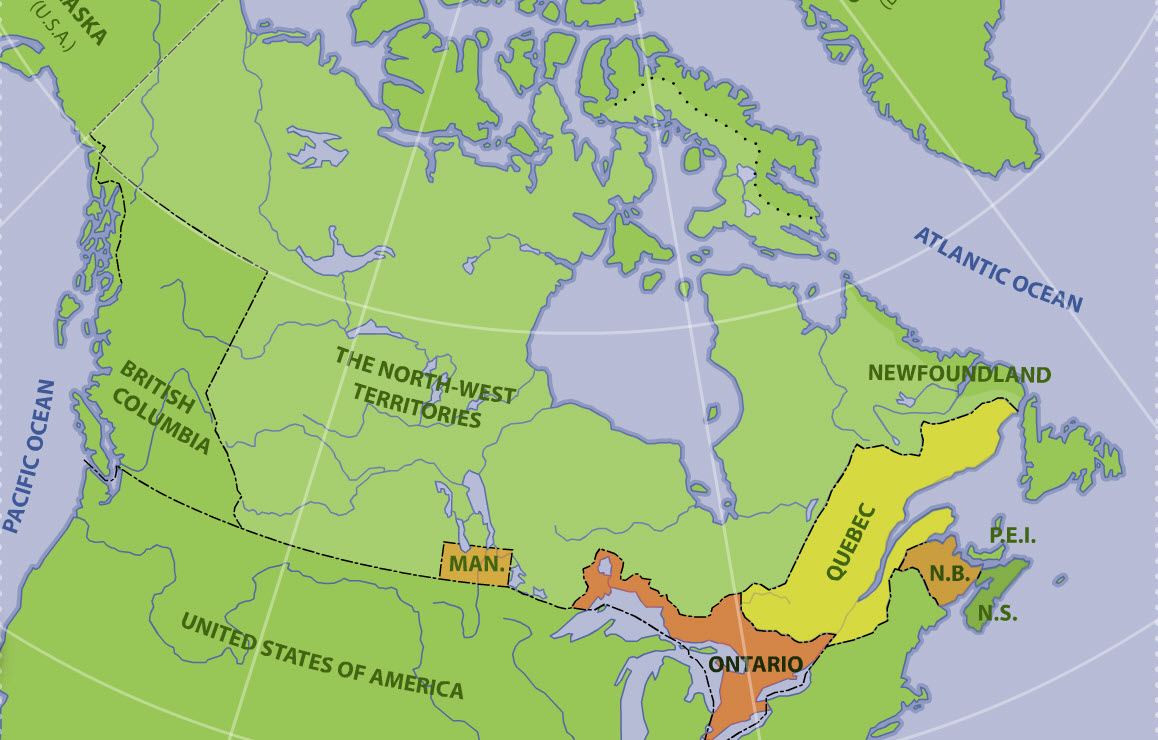
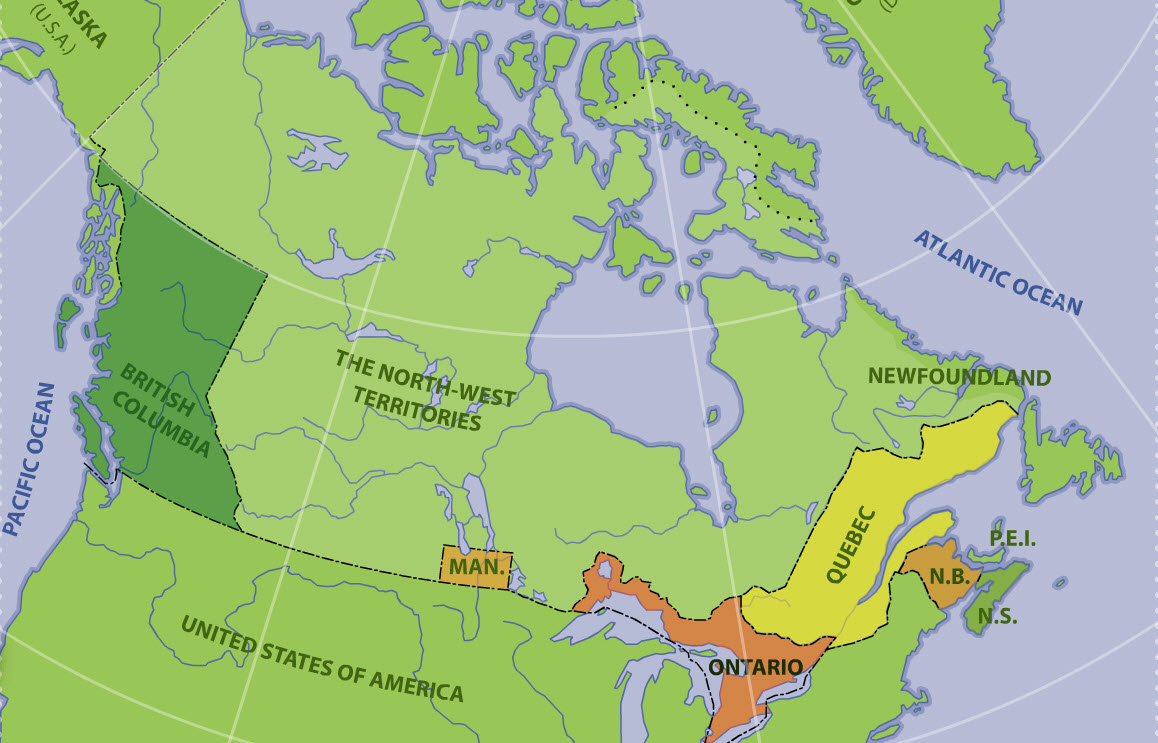
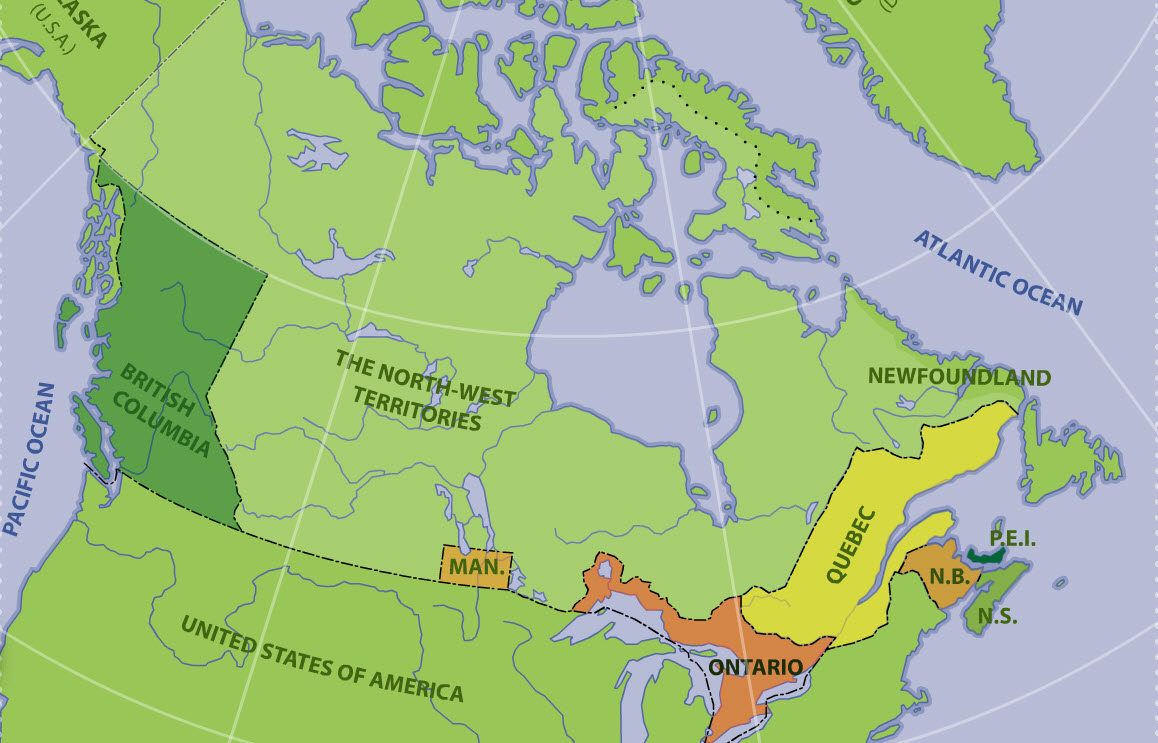
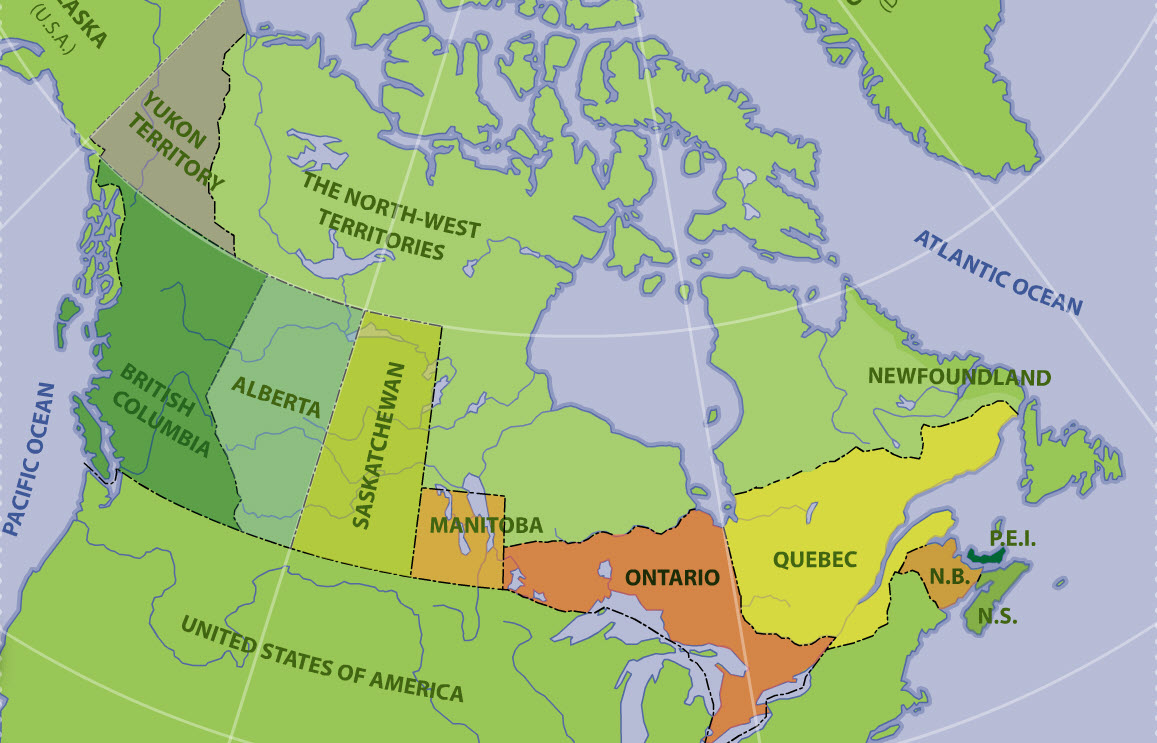
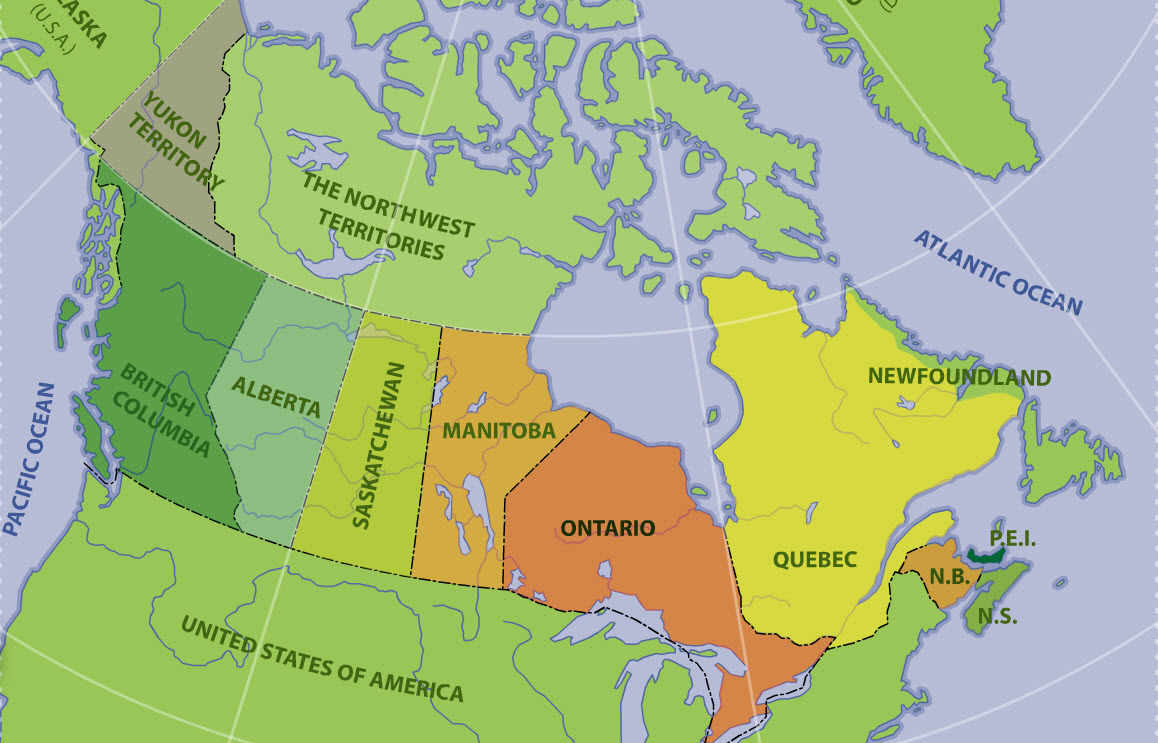
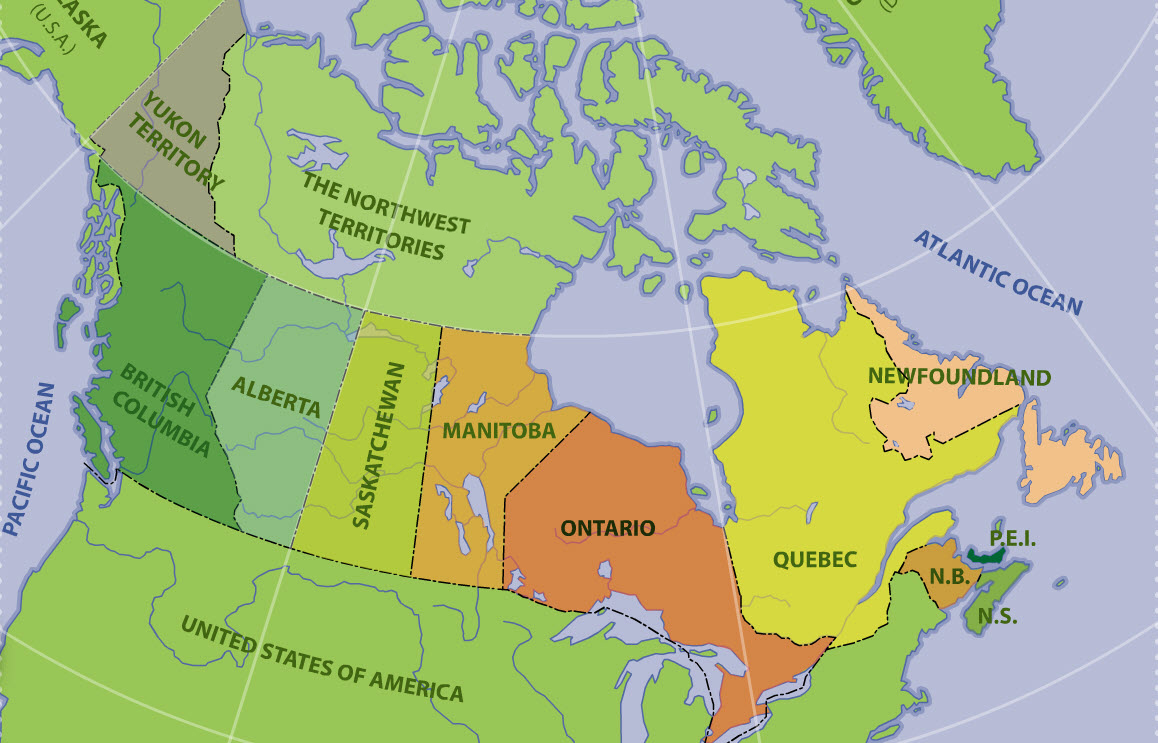
The British North America Act, 1867, also provided for the entry of other colonies into the Dominion of Canada. In 1870, part of the territory of Rupert's Land and the Northwestern Territory became Canada's fifth province - Manitoba. British Columbia's entry into Confederation in 1871 was followed by Prince Edward Island in 1873, Alberta and Saskatchewan in 1905 (which were formed out of the then North-West Territories), and Newfoundland in 1949.
Although they are legally distinct jurisdictions, Canada's three territories of Yukon, the Northwest Territories, and Nunavut are granted their powers through federal legislation instead of through the Canadian constitution. The Yukon Territory was split from the North-West Territories in 1898 and was renamed to Yukon in 2002 (the hyphen in North-West Territories would be removed in 1906). The last and most recent territory to be created was Nunavut, which was a part of the Northwest Territories until 1999.
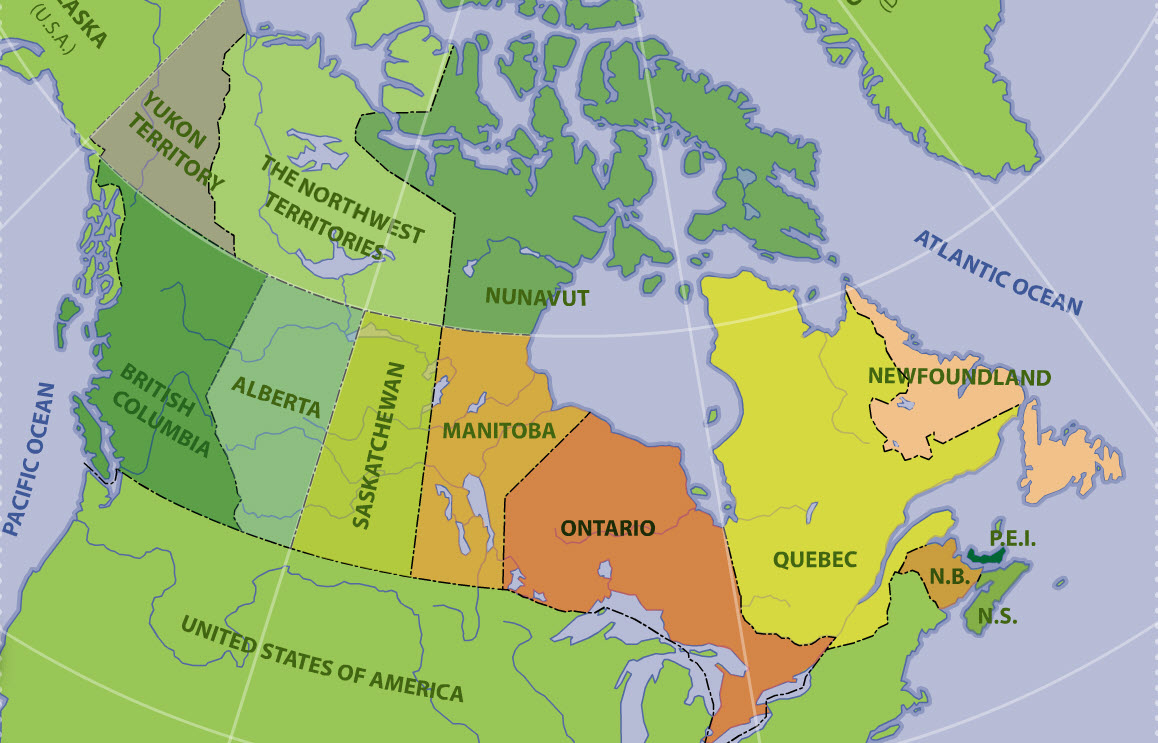
Each territory has a similar parliamentary system like that of the provinces, as well as a Commissioner with powers similar to that of a provincial Lieutenant Governor. However, in contrast to the role of the Lieutenant Governor, which is to represent the King in each of the provinces, the role of the territorial Commissioner is to represent the federal Government of Canada in each of the three territories.
